3D Urban Modeling without GIS
This project details the methodology for creating a detailed 3D urban model of central Ilam city for microclimate simulation, achieved without relying on GIS data.
Project Overview
Accurate urban models are essential for understanding and simulating microclimate conditions, especially in relation to solar potential and energy consumption. This project addresses the challenge of creating such models in areas lacking readily available GIS data.
Methodology
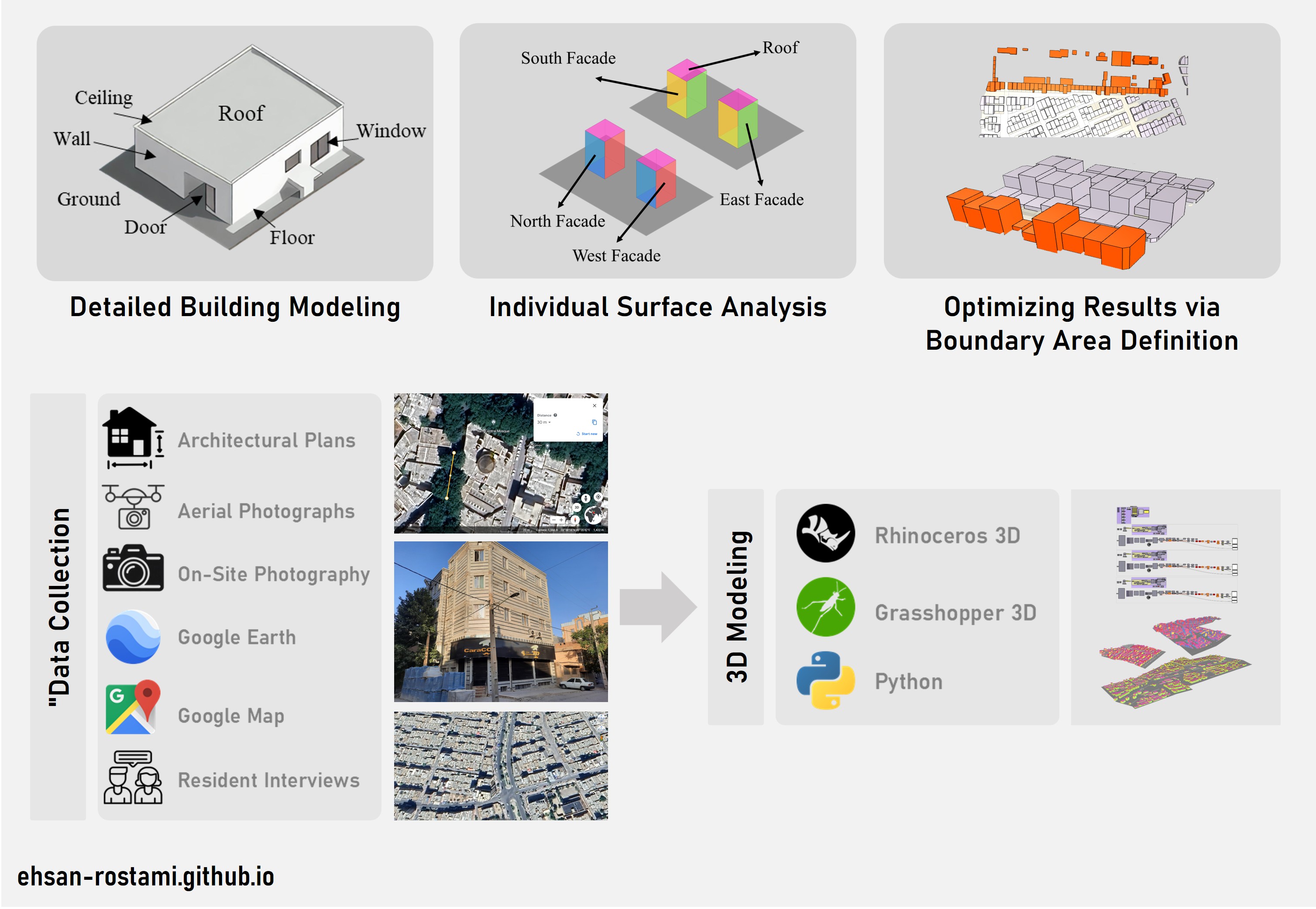
- Data Acquisition: Collection of detailed architectural plans from municipalities, high-resolution aerial photographs, and on-site photography. In some cases, information was acquired through residents and inhabitants.
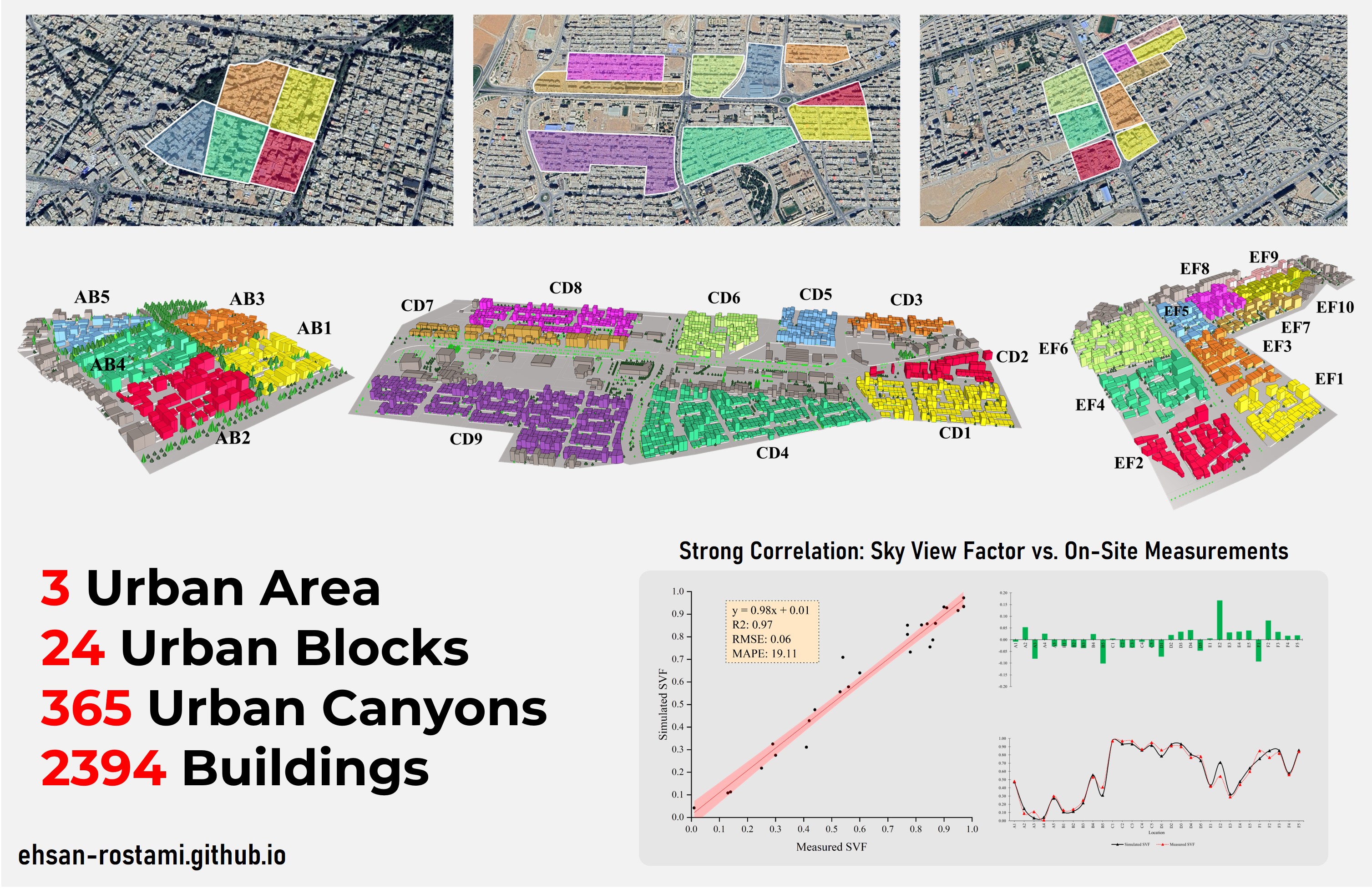
- 3D Modeling: Labor-intensive creation of approximately 2,500 building models within the urban core of Ilam city, taking approximately 8 months.
- Irregular Texture Simulation: Accurate representation of the natural irregularity in urban fabric, capturing detailed building shapes and adjacencies without assuming a simplified, regularized urban texture.
Key Innovation
The creation of a large-scale (approximately 2,500 buildings) and high-fidelity 3D urban model without utilizing GIS data represents an achievement in our field.
This methodology demonstrates a viable approach for solar potential and energy consumption research in underdeveloped regions lacking robust GIS resources, which is a common limitation, particularly in many Iranian cities, allowing detailed building information to be accurately modeled.
Key Findings
The completed 3D model enabled detailed simulation of solar potential and energy consumption, revealing how the natural irregularity of urban texture significantly influences energy performance. These findings provide crucial insights for sustainable urban planning, especially in contexts with similar data limitations.
Related Publications
This project is closely related to publications on the impact of urban morphology on solar potential and energy consumption. Please see the Publications page for more information.